Buyer's Guide for POS Card Readers
Please Note: Some of the products linked in this buyer guide might be out of date. We are working to update this documentation. Please reach out to our sales team if you have any questions.
Learn Magnetic Card Reader Basics From The Pros
 How Do Magnetic Card Readers Work?
How Do Magnetic Card Readers Work?
Magnetic card readers use similar technology to legacy tape decks and VHS players; a small sensor in the card reader measures the magnetic output from the card as it's swiped and sends the output to the computer as text data. Used for capturing credit card, employee identification, or customer loyalty data, a magnetic card reader ensures quick, error-free data entry for sensitive information.
What Kind of Magnetic Card Reader Should I Buy?
It's important to verify with your POS software provider if there are any configuration requirements or specific card readers they prefer. Otherwise, magnetic card readers are pretty interchangeable, though there is some variation in terms of readability, durability, interface, tracks supported, programmability, media types, and card encryption options.
| Readability Magnetic card readers are designed for either high volume or standard volume use. High volume card readers are equipped with components for a longer read life and are usually constructed of metal. They have a longer reading channel, which ensures a successful scan on the first pass. High volume card readers also have higher volume prices, but pay for themselves in durability and performance. They are recommended for retail environments with very high transaction volumes, such as a chain store. Standard volume card readers are fine quality card readers for normal point of sale operations. These units occasionally require an additional pass to read the card and have a shorter reading life than higher volume models. They are economical, reliable, and a popular choice for most POS systems. | |
| Durability You need to consider factors such as the environment of intended use and frequency of use when selecting a card reader. Is your POS counter in a climate controlled area or outdoors? Is it operating in an unsecured self service kiosk or only by employees? Outdoor or public use of magnetic card readers warrants a metal constructed and/or weatherproof card reader. | |
| Interface Magnetic card readers are available with three different interface options: USB, PS/2 Keyboard Wedge, and Serial. The two most commonly used are the USB and PS/2, which send information back to the computer as if it were typed on a keyboard. Card readers connected via serial interfaces may require special software to interpret the data from the card reader. Most models are available with a variety of interface choices- you will need to select the part number with the proper interface for your POS set up. | |
Back of Computer View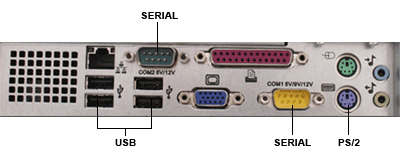 | |
Serial Connection Card Reader Example | |
USB Connection Card Reader Example | |
PS/2 Connection Card Reader Example | |
Integrated Card Reader Example | |
| Track Numbers Magnetic stripes on the back of cards can contain up to three different "tracks" of programmed information. The number of tracks used on a card depends on the type of card. Standard credit cards utilize track 1 and track 2. Track 3 may be used by other types of cards. Because magnetic card readers come in two track and three track versions, it is important to verify what information will be contained on the types of cards you may be using with your POS system. | |
| Programmability While all card readers are designed to read track 1 and track 2, or tracks 1,2, and 3 data right out of the box, most card readers can actually be programmed to divide, rearrange, edit, and validate fields of magnetic card data. Programming your card reader to change the way the data is viewed is important when running software that requires delivery of the data in a certain format. Keep in mind that using programming functionality of your card reader is an advanced feature and may require manufacturer support. | |
| Media Types All magnetic card reader units read magnetic stripes, but some manufacturers offer combination models that also feature the ability to read barcodes. There are also slot card readers designed only to read barcodes. Some examples of cards media types that may use barcodes include membership cards, and employee and student ID cards. | |
| Card Encryption Options Securing customers' credit card data is the prime focus of PCI compliance. Encrypted magnetic card readers provide greater security than readers that send plaintext data, encrypting data at the time of reading, and transmitting that encrypted data to your credit card processor. These readers must be preprogrammed by your merchant account provider, though many can be updated remotely to meet any changing requirements. | |
| Models to Try | ||||
High Volume IDTech EasyMag |
Standard Volume IDTech MiniMag |
Durability IDTech Omni |
Reads Barcodes UniTech MS146 |
Encrypted Mag-Tek Centurion Mag-Tek Centurion
|
Back to Top
For a downloadable version of this review click here